Fintech & Climate Change: How are they related?
Fintech & Climate Change: How are they related?
Fintech, or financial technology, encompasses any enterprise or business that leverages automation to provide financial services to its clientele. Although Fintech has recently gained significant traction, its roots can be traced back to the 1950s when credit cards emerged as the initial Fintech products available to the public. This innovation substantially diminished the necessity for consumers to carry physical currency. In 1998, a notable milestone occurred with the emergence of PayPal, one of the pioneering Fintech companies, which was succeeded by the introduction of online stock-trading services
But how can finance, a field generally known for numbers, and monetary flow have anything to do with sustainability, and climate change?
- Having an eco-friendly lifestyle has been the choice of many consumers in recent years. This climate-conscious community wants its financial service providers to have the same mindset and promote a sustainable outlook.
- Having an eco-consciousness can also give companies a certain edge over other competitors. Companies that ignore this lifestyle can be at risk of losing valuable consumers.
- Apart from consumers even regulatory authorities and the government have been pushing industries towards an environment-friendly world, with authorities even auditing them for greenwashing.
- Moreover, climate change is something that transcends the business world and can have a global impact. Hence they understand that their survival depends on a healthy planet
What does Fintech look like in the business world?
- Green Investment: These include Fintech companies that invest in digital solutions that promote renewable energy.
- Digital payments: Opting for digital banking can make a huge impact on the environment as it reduces the need for consumers to carry cash, cheques, or paper statements thereby totally erasing the negative impact of paper production globally.
- Green Loans & Sustainable Finance: Fintech services can provide green loans with lower interest rates to companies that support eco-friendly options.
- Carbon tracking: Carbon tracking technology can aid in monitoring carbon emissions, a crucial step in attaining global environmental objectives. Digital solutions, such as using blockchain, can offer live tracking of CO2 emissions, granting businesses the ability to effectively supervise their carbon footprint and implement proactive measures to reduce their environmental impact.

Common Fintech trends:
1. Environment-friendly cryptocurrencies: These include cryptocurrencies that require less energy, unlike Bitcoin which is estimated to consume electricity as a whole country like Thailand.
2. Digital wallets & Contactless Payments: As per studies, cash and credit cards produce an average of 3.78g of CO2 per transaction. Digital wallets can be an eco-friendly alternative for companies to reduce paper and plastic consumption, endorse renewable energy sources, and even contribute a portion of their income towards environmental causes. Contactless payments too can be linked with consumers relying on e-tickets rather than cash or paper tickets, contributing to the reduction of paper usage and the associated environmental impacts.
Fact Note: About a third of the environmental impact of the debit card payment system is caused by greenhouse gas emissions from energy consumption and transport
Does Fintech ensure safety?
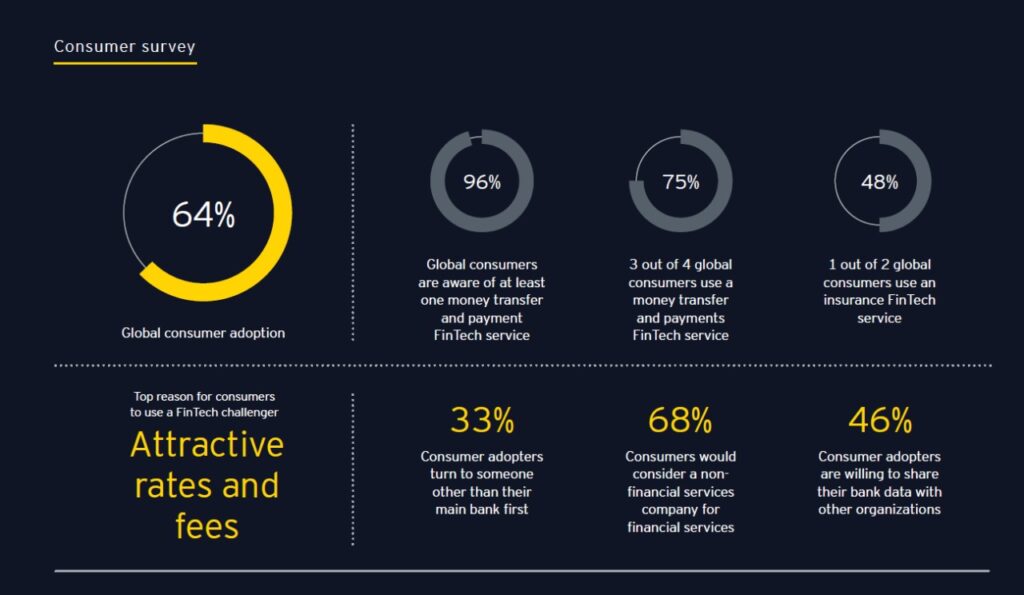
According to the data below by EY, 64% of people globally are willing to use Fintech tools. India is one of the emerging Fintech markets along with China.
Challenges encountered by Fintech industries:
1. “Green” standards are not uniform or lacking.
Numerous operational standards in the realm of green finance are either unresolved or underdeveloped. These include standards about environmental data, methodologies for calculating environmental benefits, specifications for green finance products, and guidelines on the identification of green projects.
2. Environment data quality needs improvement.
Environmental data serves as the cornerstone for conducting environmental risk analysis. The precision and reliability of environmental data play a pivotal role in determining the accuracy and efficacy of environmental risk assessments. To illustrate, inaccuracies in pollutant emissions data can lead to discrepancies between corporate public information disclosures and the actual environmental impact of a company’s pollution.
3. Low levels of professional capacity in the green finance and fintech space.
The successful integration of fintech into green finance necessitates proficient utilization of big data alongside well-established data governance mechanisms, coupled with expertise in both fintech and environmental science domains. For example, the task of evaluating green products and projects of financial institutions is a responsibility often outsourced to third-party environmental service providers. These providers, however, may lack familiarity with the intricacies of the finance sector and tend to operate with a less technologically advanced approach, resulting in increased costs and slower processes.
Fintech as a green solution is the future of the financial sector that can take the industry to a whole new level, bearing in mind that it is followed diligently. Fintech as an institution reminds us that even something as simple as financial services can shape the world around us. It allows financial services to evolve and respond to global challenges