
India's Green Hydrogen Mission: Path to a Greener Future
The Green Hydrogen Mission is a national initiative in India that aims to establish the country as a global hub for green hydrogen production, usage, and export. The mission involves promoting research and development in green hydrogen technologies, building necessary infrastructure, and creating a supportive policy and regulatory environment for the growth of the green hydrogen industry. The mission is a part of India’s strategic transition towards a sustainable and greener future.
What is Green Hydrogen?
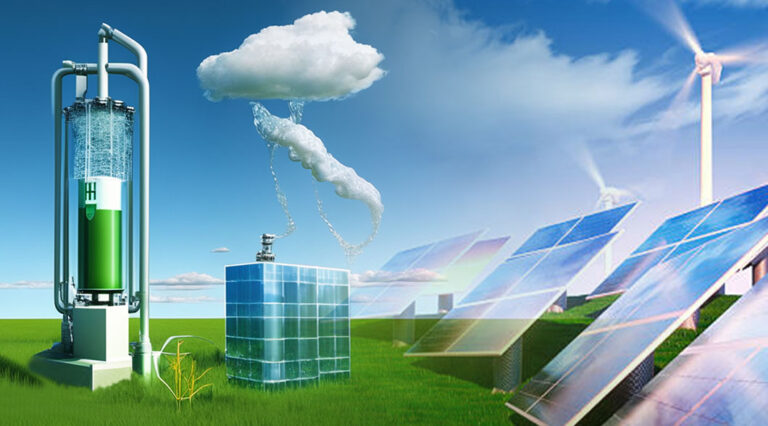

Green hydrogen is hydrogen gas produced through renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydropower using a process called electrolysis. Electrolysis involves passing an electric current through water, causing the water molecules to separate into hydrogen and oxygen. This carbon-free method distinguishes green hydrogen from grey and blue hydrogen, which are derived from fossil fuels. Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas without carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology, while blue hydrogen uses CCS to reduce carbon emissions. As a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels, green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in future energy systems.
How Green Hydrogen Works?
Producing green hydrogen requires electrolyzers powered by renewable energy sources. These devices use electricity to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen while capturing the hydrogen. Green hydrogen can be stored in high-pressure tanks, metal hydrides, or liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs), which enable safe and efficient storage.
Transportation of green hydrogen primarily relies on pipelines, trucks, and ships, with ongoing research into new methods to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impacts.
The Future of Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen holds substantial potential as a clean and sustainable energy source, with applications spanning from fuel for transportation to power generation and industrial processes.
As a crucial component in the global energy transition, green hydrogen aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and decrease dependence on fossil fuels. However, its widespread adoption depends on addressing challenges in production, storage, and transportation, alongside ensuring economic viability.
With technological advancements and an increasing focus on renewable energy sources, green hydrogen is expected to play a more significant role in the future. Experts predict that green hydrogen could supply up to 25% of the world’s energy needs by 2050, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future. Additionally, green hydrogen can help countries achieve their climate targets under the Paris Agreement, further emphasizing its importance in the global fight against climate change.
India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission

The mission focuses on research, development, and large-scale adoption of green hydrogen, aiming to harness India’s vast renewable energy potential and support the nation’s energy transition.
Key players in India’s green hydrogen industry include Larsen & Toubro, Tata Power, and Indian Oil Corporation, among others. These companies are investing in research and development, production facilities, and partnerships to strengthen India’s position in the global green hydrogen market. The mission also encourages the development of domestic manufacturing capabilities for electrolyzers, helping to boost local industries and create employment opportunities.
Applications of Green Hydrogen
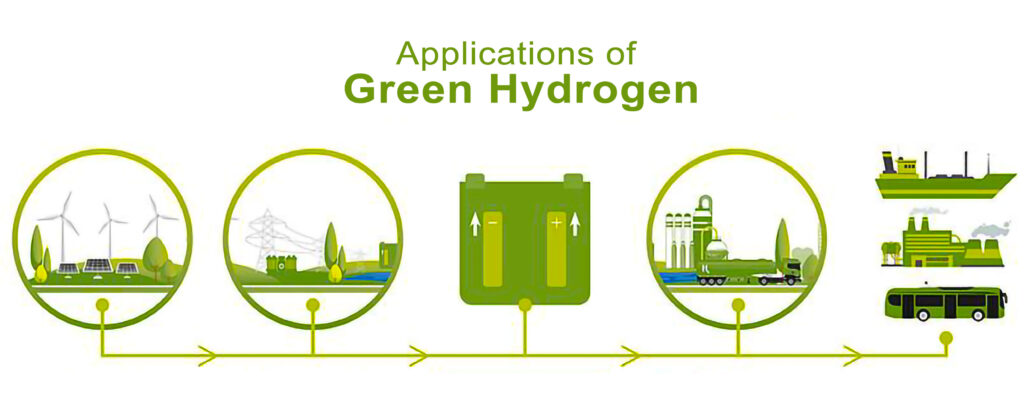
The versatility of green hydrogen makes it an attractive energy solution for various sectors. Some of its primary applications include:
- Transportation: Green hydrogen can be used as a clean fuel in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), including cars, buses, and heavy-duty trucks. FCEVs generate electricity from hydrogen through a chemical reaction with oxygen, producing water vapour as the only emission. This makes them a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- Aviation and Maritime: The aviation and maritime industries are exploring green hydrogen and its derivatives, such as ammonia and methanol, as alternative fuels. These industries face unique challenges in reducing emissions due to the energy density requirements of long-distance travel. Green hydrogen and its derivatives can help them achieve their sustainability goals and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
- Power Generation: Green hydrogen can complement intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind by providing stable and reliable power during periods of low generation. When the energy demand is higher than the available renewable energy supply, green hydrogen can be converted back into electricity through fuel cells or gas turbines. This enables efficient energy storage and utilization, promoting the integration of renewable energy into the grid.
- Industrial Processes: Green hydrogen can be used as a feedstock in energy-intensive industries, such as steel and cement production. By replacing fossil fuels with green hydrogen, these industries can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global emissions reduction targets. Green hydrogen can also serve as a feedstock for producing ammonia, methanol, and other chemicals, fostering a greener chemical industry.
Challenges and Opportunities in Green Hydrogen

Despite its immense potential, the green hydrogen industry faces several challenges that must be addressed to ensure its widespread adoption and success. Some of these challenges include:
 Production Costs: Currently, green hydrogen production costs are relatively high compared to traditional fossil fuels like petrol and diesel. The costs are more than 4-5 times higher. The cost of electrolyzers, renewable energy infrastructure, and other components required for green hydrogen production contributes to its higher price. To overcome this challenge, investments in research and development are needed to improve production technologies and reduce costs.
Production Costs: Currently, green hydrogen production costs are relatively high compared to traditional fossil fuels like petrol and diesel. The costs are more than 4-5 times higher. The cost of electrolyzers, renewable energy infrastructure, and other components required for green hydrogen production contributes to its higher price. To overcome this challenge, investments in research and development are needed to improve production technologies and reduce costs.
-
 Storage and Transportation: Storing and transporting green hydrogen presents unique challenges due to its low energy density and the need for high-pressure or cryogenic storage systems. Ongoing research in storage technologies, such as metal hydrides and LOHCs, aims to address these challenges and develop more efficient, cost-effective solutions.
Storage and Transportation: Storing and transporting green hydrogen presents unique challenges due to its low energy density and the need for high-pressure or cryogenic storage systems. Ongoing research in storage technologies, such as metal hydrides and LOHCs, aims to address these challenges and develop more efficient, cost-effective solutions. -
 Infrastructure Development: The widespread adoption of green hydrogen requires the development of extensive infrastructure, including production facilities, pipelines, refuelling stations, and more. Governments and private investors must collaborate to fund and construct the necessary infrastructure, creating an environment that supports the growth of the green hydrogen industry.
Infrastructure Development: The widespread adoption of green hydrogen requires the development of extensive infrastructure, including production facilities, pipelines, refuelling stations, and more. Governments and private investors must collaborate to fund and construct the necessary infrastructure, creating an environment that supports the growth of the green hydrogen industry. -
 Policy and Regulation: As a young industry, green hydrogen requires supportive policies and regulations to encourage investment, research, and adoption. Governments must implement policies that incentivize green hydrogen production and use, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and carbon pricing, to accelerate the transition to a green hydrogen economy.
Policy and Regulation: As a young industry, green hydrogen requires supportive policies and regulations to encourage investment, research, and adoption. Governments must implement policies that incentivize green hydrogen production and use, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and carbon pricing, to accelerate the transition to a green hydrogen economy.
Despite these challenges, the green hydrogen industry presents numerous opportunities for growth and innovation. The potential to transform the energy sector, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and contribute to a more sustainable future makes green hydrogen an attractive prospect for governments, businesses, and investors. By working together to address the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities, the world can create a thriving green hydrogen industry that benefits people, the economy, and the environment.
Requirements for the Success of India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission
Need for Public Awareness and Engagement
Green hydrogen offers a promising pathway to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. By addressing the challenges and harnessing the opportunities, the world can realize the full potential of green hydrogen and make significant strides in combating climate change. Education, public awareness, and engagement are essential components of this journey, empowering individuals and communities to contribute to the global effort to build a greener, more prosperous future.
Need for Investment and Financing
The green hydrogen industry requires significant investments to achieve its potential. Governments, private investors, and financial institutions must come together to provide the necessary capital for green hydrogen projects, including research and development, infrastructure construction, and skills training.
Public-private partnerships can be an effective way to mobilize investments and share risks, making green hydrogen projects more attractive to investors. Additionally, governments can use financial instruments such as grants, loans, and guarantees to support green hydrogen initiatives.
Green bonds and other innovative financing mechanisms can also play a crucial role in raising capital for green hydrogen projects. By leveraging these financial tools, green hydrogen projects can access the funds they need to develop and scale, contributing to the industry’s overall growth and success.
Conclusion

Green hydrogen has the potential to revolutionize the global energy landscape by offering a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission is a significant step in this direction, focusing on research, development, and large-scale adoption of this promising energy source. Despite the challenges, green hydrogen’s potential to transform the energy sector and contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future remains an exciting prospect for India and the world.

